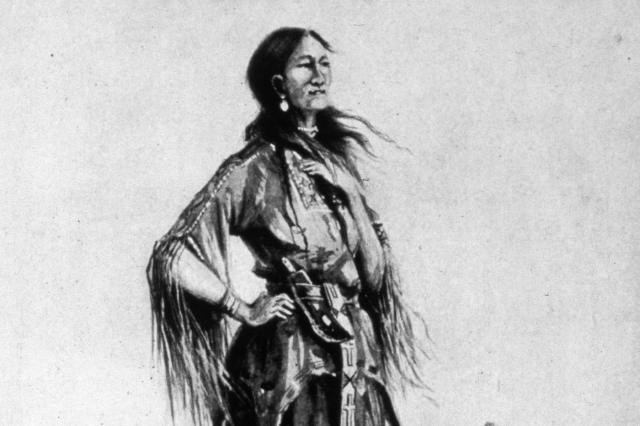
5 Indigenous Leaders You Should Know
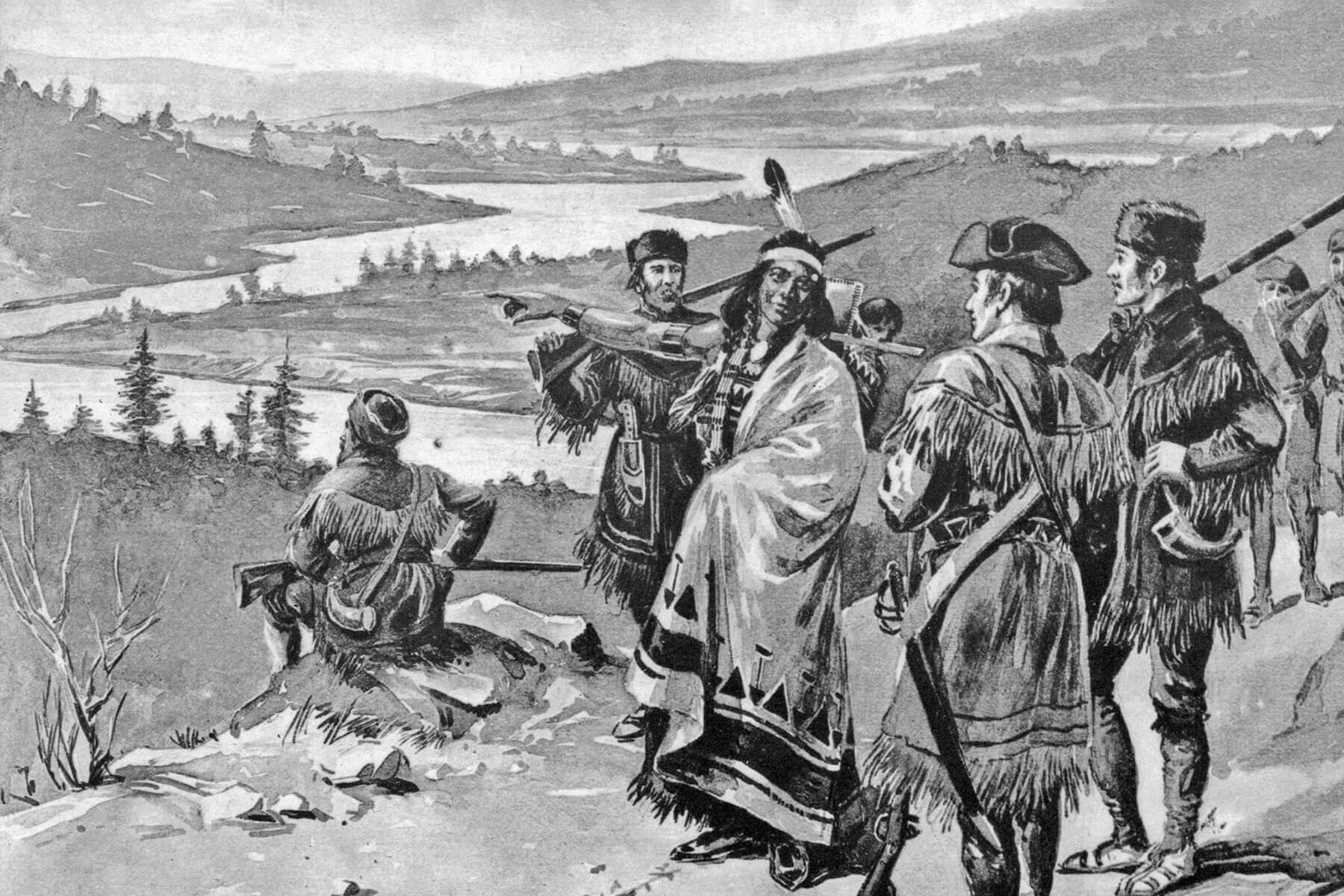
As we look back at American history, it’s crucial to take a moment to reflect on and recognize the contributions made by the nation’s Indigenous peoples, who are so often overshadowed by famous figures who came to the United States from other parts of the world. To commemorate this important part of America’s heritage, here’s a look at five notable Indigenous heroes and leaders who shaped the nation through their tireless efforts.
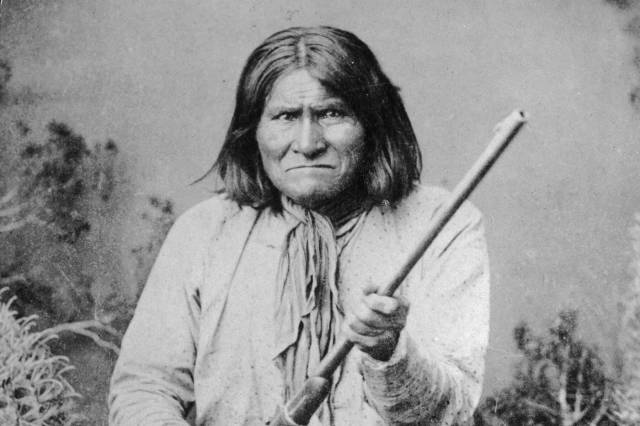

Geronimo (1829-1909)
A medicine man and leader of the Bedonkohe band of the Chiricahua Apache, Geronimo was born on the Gila River in New Mexico, where he was originally given the name Goyahkla, meaning “the one who yawns.” After the United States government forcibly relocated 4,000 Apaches to a reservation in San Carlos, Arizona, Geronimo led dozens of breakouts in an effort to return his community to their nomadic roots. Geronimo’s legacy is vast. His relationship with many American and Mexican civilians was complex, as he fought against colonialism but was made famous after appearing in Buffalo Bill’s “Wild West” sideshow and eventually in Theodore Roosevelt’s election parade. Geronimo’s tireless fight for Apache independence cemented him as a fearless crusader for freedom by the time of his death from pneumonia in 1909.
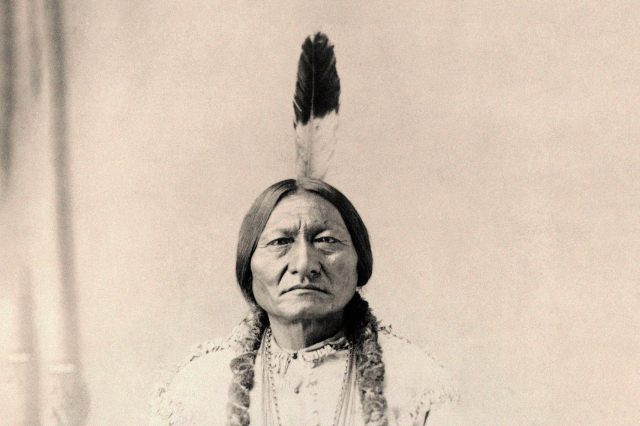

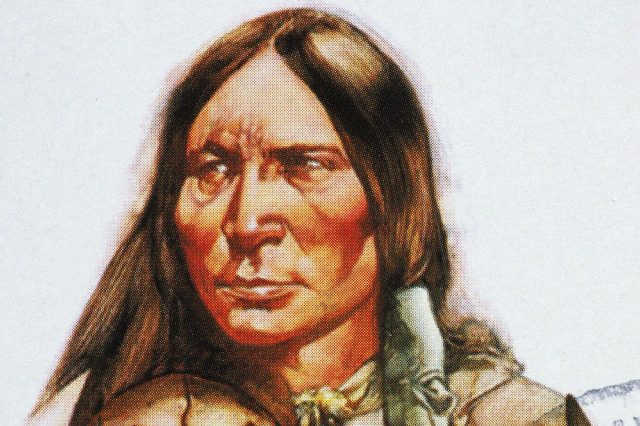
Sitting Bull (c. 1831-1890)
The son of a warrior, Sitting Bull was born in what is now South Dakota and was nicknamed “Slow” for his lack of fighting ability — that is, until he was branded Tatanka Yotanka (“Sitting Bull”) at age 14 after “counting coup” in a battle against the Crow Tribe. (“Counting coup” is a way to humiliate an enemy by riding close enough to touch them with a stick.) Sitting Bull eventually rose to become chief of the Hunkpapa Sioux, and fought tirelessly against the U.S. military, who sought to seize Indigenous land.
After fleeing to Canada to escape a vengeful army in the wake of the defeat of General George Armstrong Custer (and his 210 troops) in 1876 at the Battle of Little Bighorn, Sitting Bull returned to the U.S. in 1881 and was held prisoner at Standing Rock Reservation on Dakota Territory. His impact, however, could not be contained: After an Indigenous mystic claimed in 1889 that a ghost dance would eliminate the threat of white settlers on Native land, Sitting Bull allowed his followers to practice the dance — much to the horror of federal officials, who feared another uprising. Sitting Bull was killed by gunfire upon his arrest in 1890, and is remembered as a martyr for freedom.