6 Inventions Often Credited to the Wrong Person
There’s nothing more frustrating than working your socks off only to see someone else get all the credit for your efforts. Spare a thought, then, for the minds behind some of history’s most significant innovations, who, despite months, years, or in some cases lifetimes of work, find someone else’s name ignominiously attached to their invention.
Sometimes inventions are miscredited in the public consciousness simply because a more famous name becomes associated with the creation. For example, Thomas Edison and Henry Ford — two of modern history’s most well-known innovators — are often credited with things they didn’t actually invent, through no fault of their own. Then there are the more insidious misattributions. In some instances, an idea has been copied or outright stolen, robbing the true inventor of their glory; in others, a more senior or prominent member of a team is given credit despite not coming up with the original idea. See, for example, the Matilda effect, in which notable discoveries made by women have often been misattributed to the men they worked with.
Here are some notable inventions in history that are frequently credited to the wrong person, from the flush toilet to the iPod.
The Flush Toilet
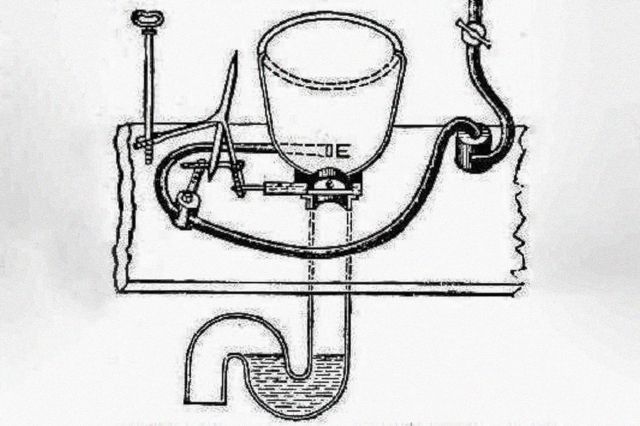
No name in the history of toilets is more famous than that of plumber Thomas Crapper, partly because his name appeared on the once-ubiquitous Crapper brand of toilets, and partly because Crapper is a humorously appropriate name for a toilet (the slang word “crap” existed before Thomas Crapper). Crapper, however, did not invent the flushing device with which he is so associated. He did patent the U-bend and floating ballcock — key components of the modern toilet — in the late 1880s, but he never held a patent for the flush toilet. Much earlier, in 1596, John Harington, an English courtier and the godson of Queen Elizabeth I, described what can be considered the first flush toilet, which involved a 2-foot-deep bowl and a massive 7.5 gallons of water per flush. (Only two working models were made, one in Haringon’s own home and one in Queen Elizabeth’s palace.) The first patent for a flushable toilet was granted to the Scottish inventor Alexander Cumming in 1775.

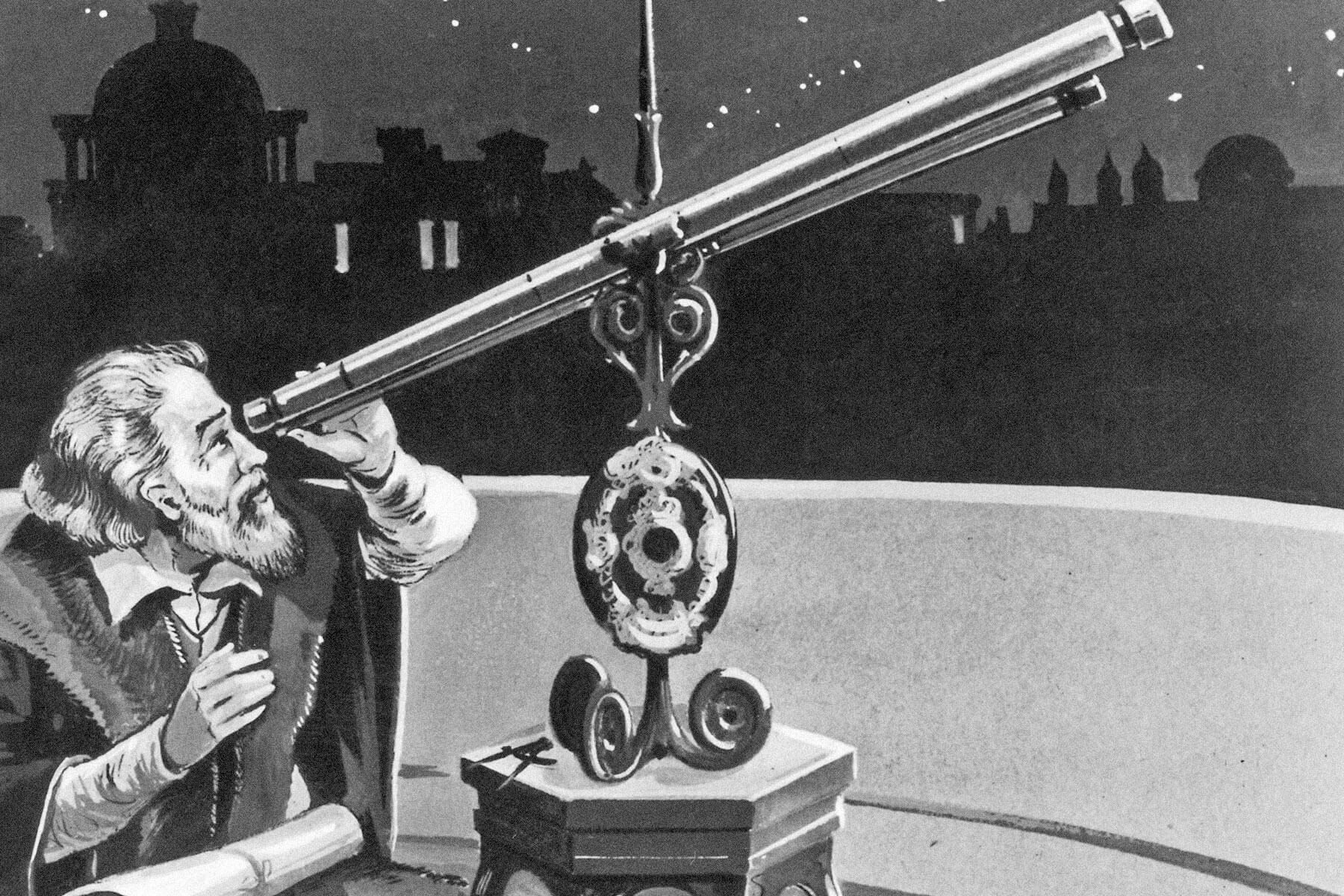
The Telescope
The Italian polymath Galileo Galilei is often credited with inventing the telescope, and it’s easy to see why. He gave birth to modern astronomy with his telescope-assisted discoveries about our moon, the moons of Jupiter, and other celestial bodies. Galileo made his first telescope in 1609 after hearing about the “perspective glasses” being made in the Netherlands. But the first person to apply for a patent for a telescope was Dutch eyeglass-maker Hans Lippershey in 1608, a year before Galileo. His telescope could magnify objects only three times, but it was nonetheless a landmark in the history of optics. (By comparison, by the end of 1609, Galileo had developed a telescope that magnified objects 20 times.) Whether Lippershey should be credited as the inventor of the telescope remains an open debate, as it is entirely possible that others created similar devices before he filed his patent.