7 Fascinating Facts From the History of the World’s Fair
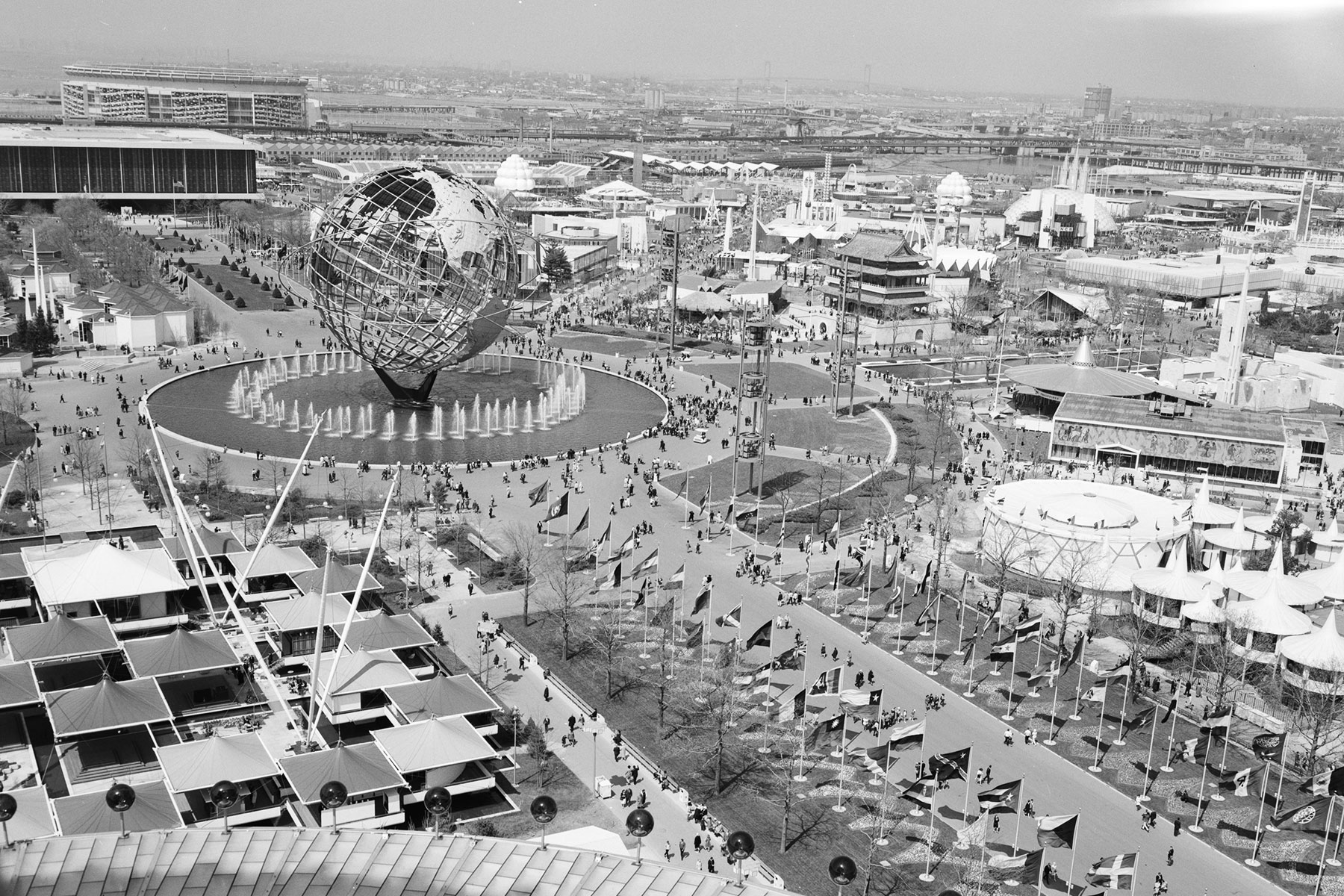
The first world’s fair, known as the Great Exhibition, took place in London in 1851. Held in the Crystal Palace — a massive exhibition hall made of glass and iron — the fair displayed marvels of industry and science as well as works of craftsmanship and art from around the world. Since then, more than 100 world’s fairs have been held in over 20 countries, and countless inventions have made their debut at these massive events, from the telephone to cotton candy. Though the world’s fair has declined in popularity in the United States, it remains popular throughout much of the rest of the world. Here are seven highlights from the history of these fascinating exhibitions.
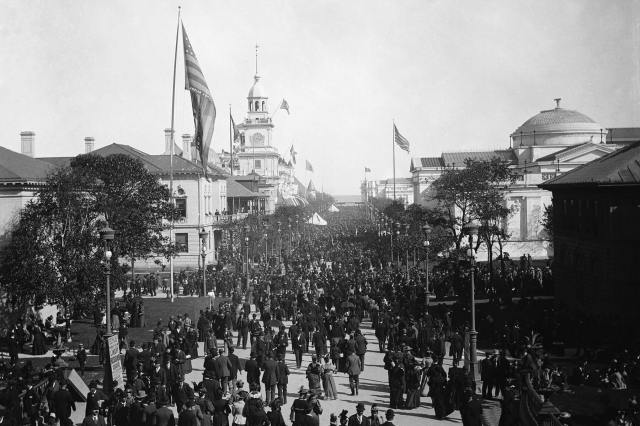

One Fair Sparked a Frenzy for Plastic Pickles
The 1893 World’s Columbian Exposition in Chicago (named in honor of Christopher Columbus) was ripe with opportunity for food sellers. But H.J. Heinz — an American purveyor of pickles and ketchup — was frustrated with his booth placement. While the main floor showcased food exhibits from Germany, Great Britain, Mexico, and other nations, Heinz was stuck on the second floor where there was little foot traffic. He devised a marketing plan that promised a free prize to anyone who visited his booth: a small green plastic pickle pin. The pins were a massive hit; the crowds that flocked to his booth were so large that the floor reportedly sagged around the display. By the end of the exhibition, Heinz had given away more than 1 million pickle pins, paving the way for his brand to become a household name.
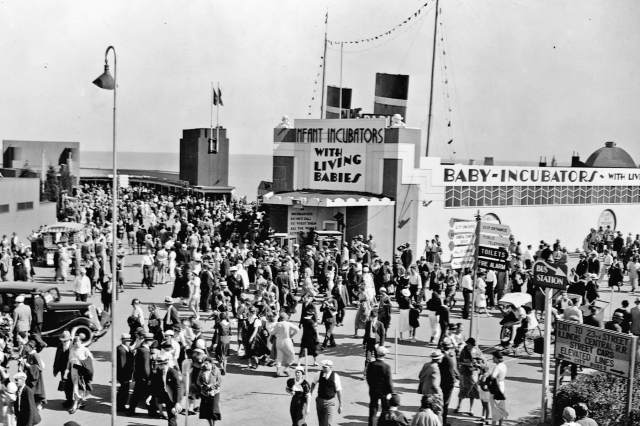

Baby Incubators Started as a Carnival Attraction
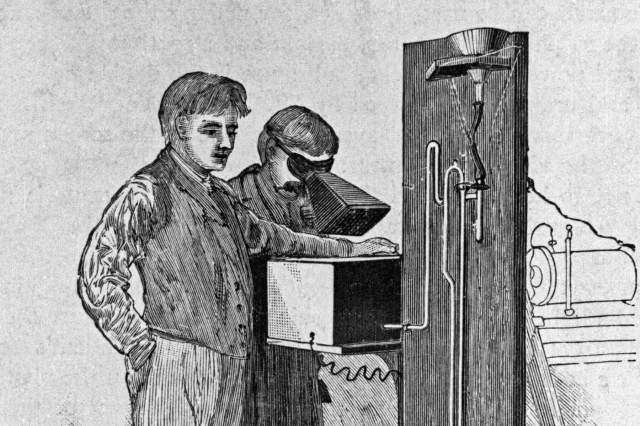
The baby incubator — a lifesaving device in which premature or sick infants can develop — was invented in the 19th century by French obstetrician Stéphane Tarnier, who got the idea after seeing baby chicks being incubated at a zoo. The invention was widely adopted decades later, thanks to the work of two men, Pierre Budin and Martin Couney. Determined to popularize the groundbreaking technology, Budin and Couney displayed six incubators complete with real premature babies at the 1896 Great Industrial Exposition of Berlin, in an exhibit they dubbed “Child Hatchery.” The exhibit was so popular that Couney went on to set up a permanent exhibit in an unlikely location: the Coney Island amusement park in New York. For the next four decades, Couney managed a neonatal intensive care unit that saved thousands of babies while doubling as a carnival attraction. Despite not being a licensed doctor, Couney is now widely credited with the adoption of the baby incubator into mainstream medicine.